5400 Laurel Springs Pkwy Suite 604 Suwanee, GA 30024

Complete Anatomy of a Diamond
-

Cut
Cut not only refers to the shape of the diamond, but also to the diamond’s proportions, symmetry and polish. The major components are the crown, girdle and pavilion. A round brilliant cut diamond has 57 or 58 facets, the 58th being the tiny flat facet at the bottom of the pavilion. The large, flat facet on the top is the table. The diamond’s proportions pertain to the relationships between table size, crown angle and pavilion depth. The combination of these relationships ultimately affects a diamond’s interaction with light.
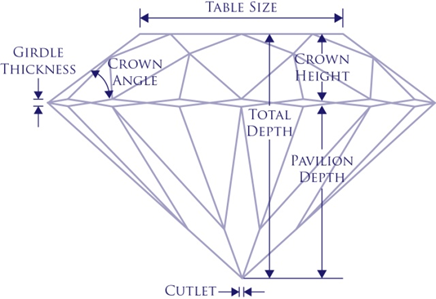
The distance from the girdle to the cutlet is known as the pavilion depth. An ideal cut diamond will reflect light off of one mirror-like facet to another, directing more light through the crown. If the pavilion depth is too shallow or too deep, light can escape through the bottom or sides of the diamond. This will make the diamond appear less brilliant.

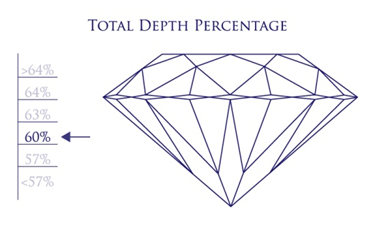
The proportions between the pavilion depth and table width also contribute to a diamond’s brilliance. To get the depth percentage, divide the pavilion depth of your diamond by the table width in millimeters. The optimal depth percentage for a round brilliant cut stone is between 57% and 64%.
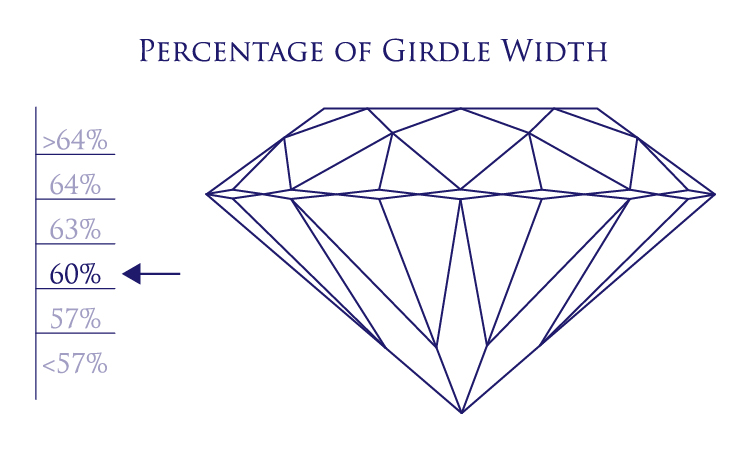
The table percentage refers to the proportions between the table width and the girdle width. The table width will never be the same width as the girdle because the crown angle takes up some of the percentage. The optimal table percentage is between 54% and 64%.
Clarity
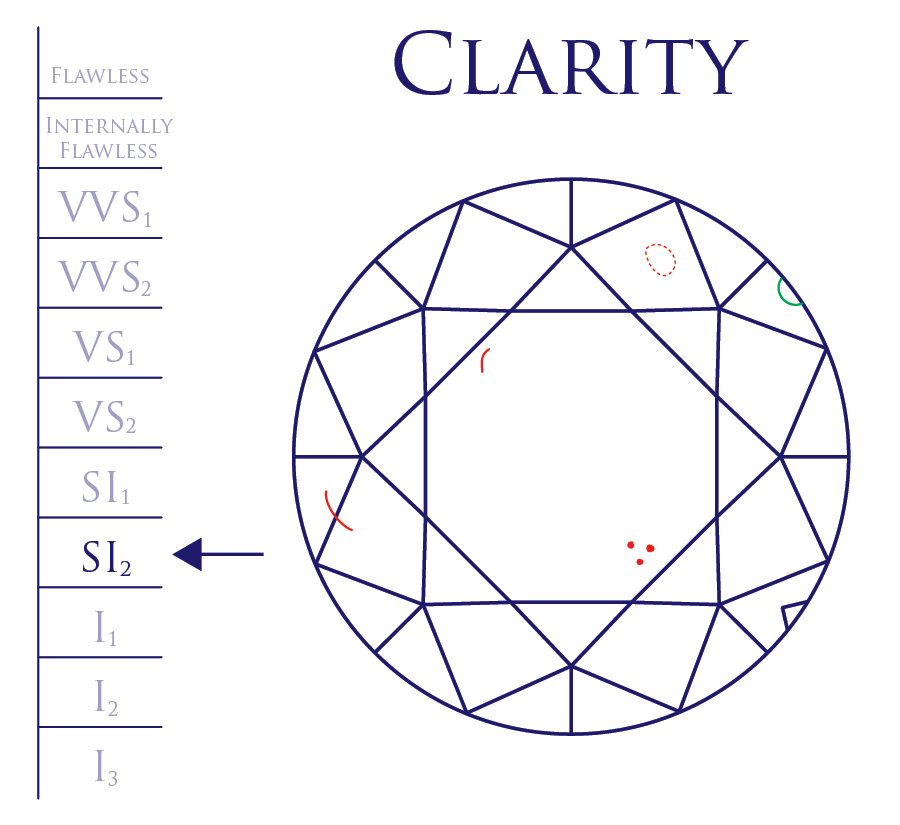
Diamond clarity refers to the absence or existence of visible flaws. Because diamonds are formed deep within the earth, under extreme heat and pressure, they often contain unique birthmarks, either internal (inclusions) or external (blemishes). Each of these flaws, including those that can only be seen under magnification, affects the brilliance of a diamond, therefore effecting its value. Diamonds are assigned a clarity grade, ranging from Flawless (FL) to diamonds with obvious inclusions (I3).
Color
The color of a diamond is an important factor when choosing a diamond. The color scale extends from D (colorless) to Z (light yellow or brown). While most people think of quality diamonds as colorless, they are very rare. Most diamonds used in jewelry have some tint of yellow or brown.

Carat Weight
While gold and platinum are weighed in grams, diamonds are weighed in carats. One carat equals 200 milligrams in weight. Contrary to popular belief, carat weight does not refer to the actual diameter of the stone. Two diamonds of the same carat weight could look like two very different size stones if one is a much deeper cut than the other. This is why it is important to consider all aspects of the diamond when selecting a stone.

